Targeted sequencing allows you to sequence only the specific genomic regions you are interested in, such as a targeted gene panel. It is very cost effective and more accurate than whole genome sequencing for the detection of SNPs, indels and known fusions as well as some rare mutations in the target gene regions due to the affordability of much deeper sequencing.
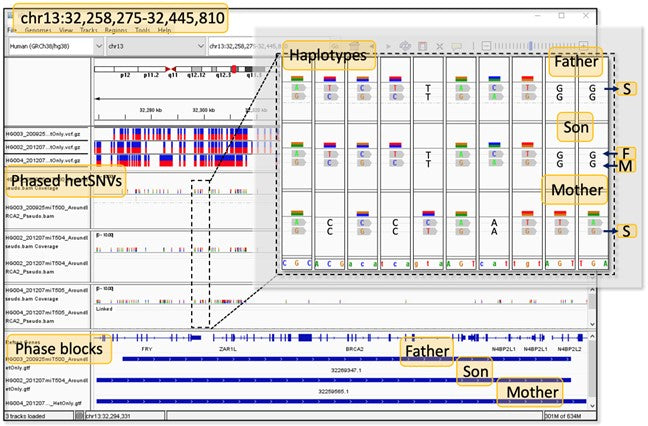
In the human genome, heterozygous sites refer to genomic positions with different alleles or nucleotide variants on the maternal and paternal chromosomes. Resolving these allelic differences across chromosomal copies, also known as phasing, is achievable on a short-read sequencer using TELL-Seq™ library preparation that captures long-range genomic information with the aid of molecular identifiers (linked read barcodes). TELL-Seq™ works not just for whole genome phasing but also for targeted phasing, enabling accurate haplotype resolution and comprehensive detection of all variant types, including areas of high homology and GC-rich regions as well as complex gene families like HLA. TELL-Seq™ library prep requires super low DNA input, especially suitable for low yield gene enrichment methods, such as CRISPR/Cas9-mediated enrichment.
Due to the major differences in DNA fragment size and quantity between whole genome sequencing and targeted sequencing, the TELL-Seq™ library prep protocols are different too. We provide user guides for two common enrichment approaches: 1) Enriching target genomic content before TELL-Seq™ library prep and 2) Enrichment after TELL-Seq™ library prep. The article published on Nature Scientific Reports demonstrates how TELL-Seq™ is used to phase targeted genes of different DNA fragment sizes on Illumina sequencer (Targeted phasing of 2–200 kilobase DNA fragments with a short-read sequencer and a single-tube linked-read library method (2024) (UST)).
Flyers and Brochures
User Guides
TELL-Seq™ Amplicon Phasing Library Prep User Guide
TELL-Seq™ Target Enrichment User Guide
User Experience Webinars
-
 Watch the webinar
Watch the webinarTargeted Phasing of the PMS2 Gene in Clinical Use
For Targeted Region < 50Mb
-
TELL-Seq™ Microbial Library Prep Kit STD24, RUO
Regular price $1,800.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
TELL-Seq™ Microbial Library Prep Kit STD8, RUO
Regular price $1,330.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
TELL-Seq™ Microbial Library Prep Kit HT144, RUO
Regular price $6,650.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per
For Targeted Region > 50Mb
-
TELL-Seq™ Library Prep Kit STD4, RUO
Regular price $900.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
TELL-Seq™ Library Prep Kit HT24, RUO
Regular price $4,490.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
TELL-Seq™ Library Prep Kit HT96, RUO
Regular price $16,260.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per
Target Blocker
-
TELL-Seq™ Target Blocker Kit, 8rxn, RUO
Regular price $125.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per
Multiplex Primers
-
TELL-Seq™ Library Multiplex Primer (1-8) Kit, RUO
Regular price $125.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
TELL-Seq™ Library Multiplex Primer C-series (1-96) Plate, RUO
Regular price $625.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
TELL-Seq™ Library Multiplex Primer (9-16) Kit, RUO
Regular price $125.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
TELL-Seq™ Library Multiplex Primer (17-24) Kit, RUO
Regular price $125.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per
Illumina Custom Sequencing Primers
-
TELL-Seq™ Illumina Sequencing Primer Kit, RUO
Regular price $100.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
TELL-Seq™ Illumina Sequencing Primer Kit HT, RUO
Regular price $275.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per